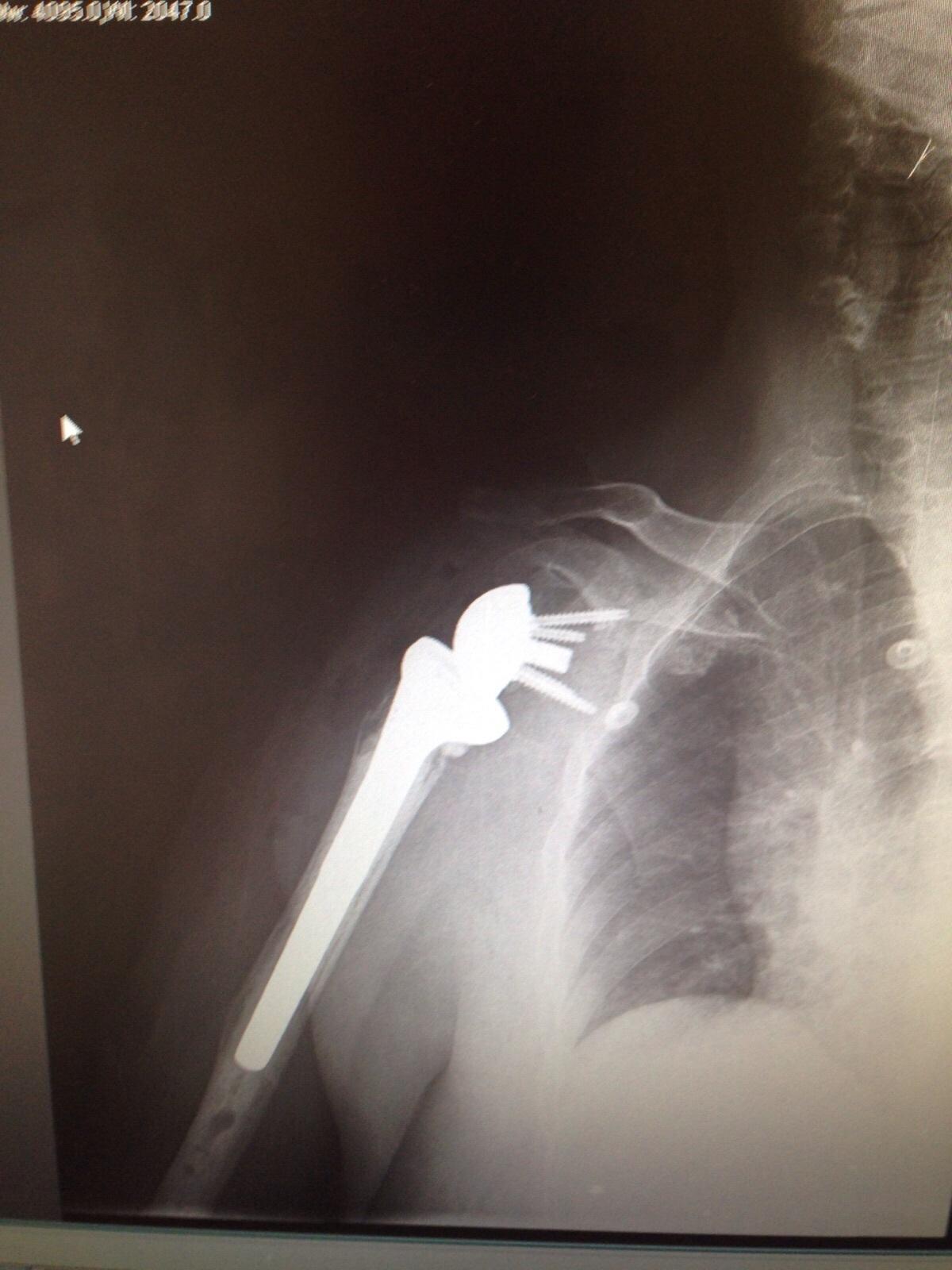
Shoulder Arthroplasty
Fuente
Este artículo es originalmente publicado en:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29665605
https://www.thieme-connect.de/DOI/DOI?10.1055/s-0043-118043
De:
Krukenberg A, Imiolczyk JP, Moroder P, Scheibel M.
Z Orthop Unfall. 2018 Apr;156(2):227-238. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-118043. Epub 2018 Apr 17.
Todos los derechos reservados para:
© 2018 Georg Thieme Verlag KG
Abstract
Shoulder arthroplasty has been performed increasingly during the last years. The concept of modern anatomic shoulder arthroplasty is based on C. S. Neer’s first shoulder prosthesis in the 1950s which was originally designed for the treatment of fractures of the proximal humerus. Since then, this monoblock prosthesis has undergone many changes and improvements. By now, an anatomic reconstruction of the joint is possible. Hence, the indications for anatomic shoulder arthroplasty have been added amongst others by osteoarthritis, necrosis, rheumatoid arthritis or posttraumatic arthritis. For years stemmed shoulder arthroplasty has been state of the art with a good clinical and radiological outcome. Nevertheless, stem-related problems occurred leading to the invention of short-stem and stem-free shoulder prosthesis. Stem-free shoulder arthroplasty allows an even better anatomic reconstruction and therefore offers more opportunities, e.g. in a severe posttraumatic status. Only short- to midterm results are published so far but those are very convincing indicating that stem-free shoulder arthroplasty is the future. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty has its origin in the 1980s. Paul Grammont invented a reversed shoulder prosthesis for patients suffering from cuff arthropathy. The center of rotation is medialised and inferiorised using the pre-loading of the deltoid muscle to move the shoulder joint. The initial prosthesis had undergone many variations as well but in contrast to anatomic shoulder arthroplasty biomechanics is still discussed a lot in reverse shoulder arthroplasty; especially in terms of finding the right inclination angle or how to prevent instability or scapular notching. This article gives a review about indications, concepts and complications of shoulder arthroplasty.
Key words
anatomic shoulder arthroplasty – reverse shoulder arthroplasty – shoulder arthroplasty – stem – stem-free prosthesis – omarthrosis
Resumen
La artroplastia de hombro se ha realizado cada vez más durante los últimos años. El concepto de la artroplastia anatómica moderna de hombro se basa en la primera prótesis de hombro de C. S. Neer en la década de 1950, diseñada originalmente para el tratamiento de fracturas del húmero proximal. Desde entonces, esta prótesis monobloque ha sufrido muchos cambios y mejoras. Por ahora, es posible una reconstrucción anatómica de la articulación. Por lo tanto, las indicaciones para la artroplastia anatómica del hombro se han agregado, entre otros, a la osteoartritis, la necrosis, la artritis reumatoide o la artritis postraumática. Desde hace años, la artroplastia de hombro ha sido un estado de la técnica con un buen resultado clínico y radiológico. Sin embargo, se produjeron problemas relacionados con el tallo que condujeron a la invención de prótesis de hombro de tallo corto y sin tallo. La artroplastia de hombro sin tallo permite una reconstrucción anatómica aún mejor y, por lo tanto, ofrece más oportunidades, p. en un estado postraumático grave. Hasta ahora solo se han publicado resultados de corto a mediano plazo, pero son muy convincentes, lo que indica que la artroplastia de hombro sin vástago es el futuro. La artroplastia de hombro inversa tiene su origen en la década de 1980. Paul Grammont inventó una prótesis de hombro invertida para pacientes que sufren de artropatía del manguito. El centro de rotación se medializa e inferioriza utilizando la precarga del músculo deltoides para mover la articulación del hombro. La prótesis inicial también había sufrido muchas variaciones, pero en contraste con la artroplastia anatómica del hombro, la biomecánica todavía se discute mucho en la artroplastia de hombro invertida; especialmente en términos de encontrar el ángulo de inclinación correcto o cómo prevenir inestabilidad o muescas escapulares. Este artículo brinda una revisión sobre las indicaciones, los conceptos y las complicaciones de la artroplastia de hombro.
Palabras clave:
artroplastia de hombro anatómica – artroplastia de hombro invertida – artroplastia de hombro – vástago – prótesis sin vástago- omartrosis