Glenoid Bone Loss in Primary RTSA: Management Options and Outcomes
Fuente
Este artículo es originalmente publicado en:
https://icjr.net/articles/glenoid-bone-loss-in-primary-rtsa-management-options-and-outcomes
De:
Author Information
Andrew R. McNamara, MD; Rowan J. Michael, MD; Thomas W. Wright, MD; Bradley S. Schoch, MD; and Joseph J. King III, MD, are from the Department of Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation at the University of Florida in Gainesville.
Todos lops derechos reservados para:
© International Congress for Joint Reconstruction
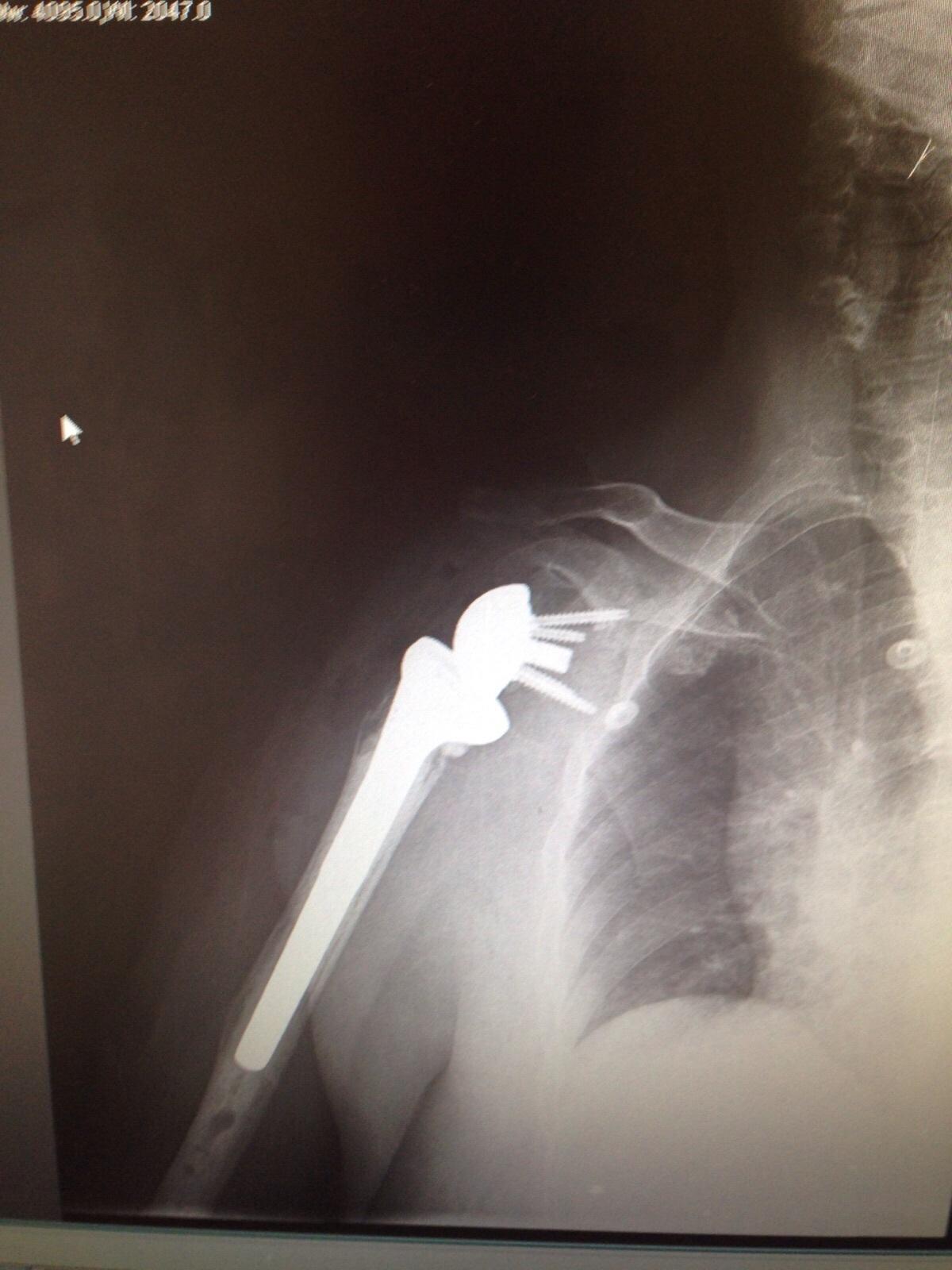
Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty has become a reliable, successful operation for treating rotator cuff arthropathy. Concomitant glenoid bone loss creates special challenges that surgeons need to be prepared to overcome.
Introduction
Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty (RTSA) has provided a reliable reconstruction option for older patients with a deficient rotator cuff and glenohumeral osteoarthritis. The reverse prosthesis is a semi-constrained implant, and unlike implants used for an anatomic total shoulder, it does not rely on rotator cuff soft tissue balancing for success.
Despite this advantage, reverse prosthesis implantation remains challenging in patients with glenoid bone loss. This article reviews the treatment options for bone loss when performing RTSA.
La artroplastia total reversa de hombro se ha convertido en una operación confiable y exitosa para tratar la artropatía del manguito de los rotadores. La pérdida concomitante de hueso glenoideo crea desafíos especiales que los cirujanos deben estar preparados para superar.
Introducción
La artroplastia total reversa de hombro (RTSA) ha proporcionado una opción de reconstrucción confiable para pacientes mayores con un manguito de los rotadores deficiente y osteoartritis glenohumeral. La prótesis reversa es un implante semirrestringido y, a diferencia de los implantes utilizados para un hombro anatómico total, no depende del equilibrio del tejido blando del manguito rotador para tener éxito.
A pesar de esta ventaja, la implantación de prótesis reversas sigue siendo un desafío en pacientes con pérdida ósea glenoidea. Este artículo revisa las opciones de tratamiento para la pérdida ósea al realizar RTSA.