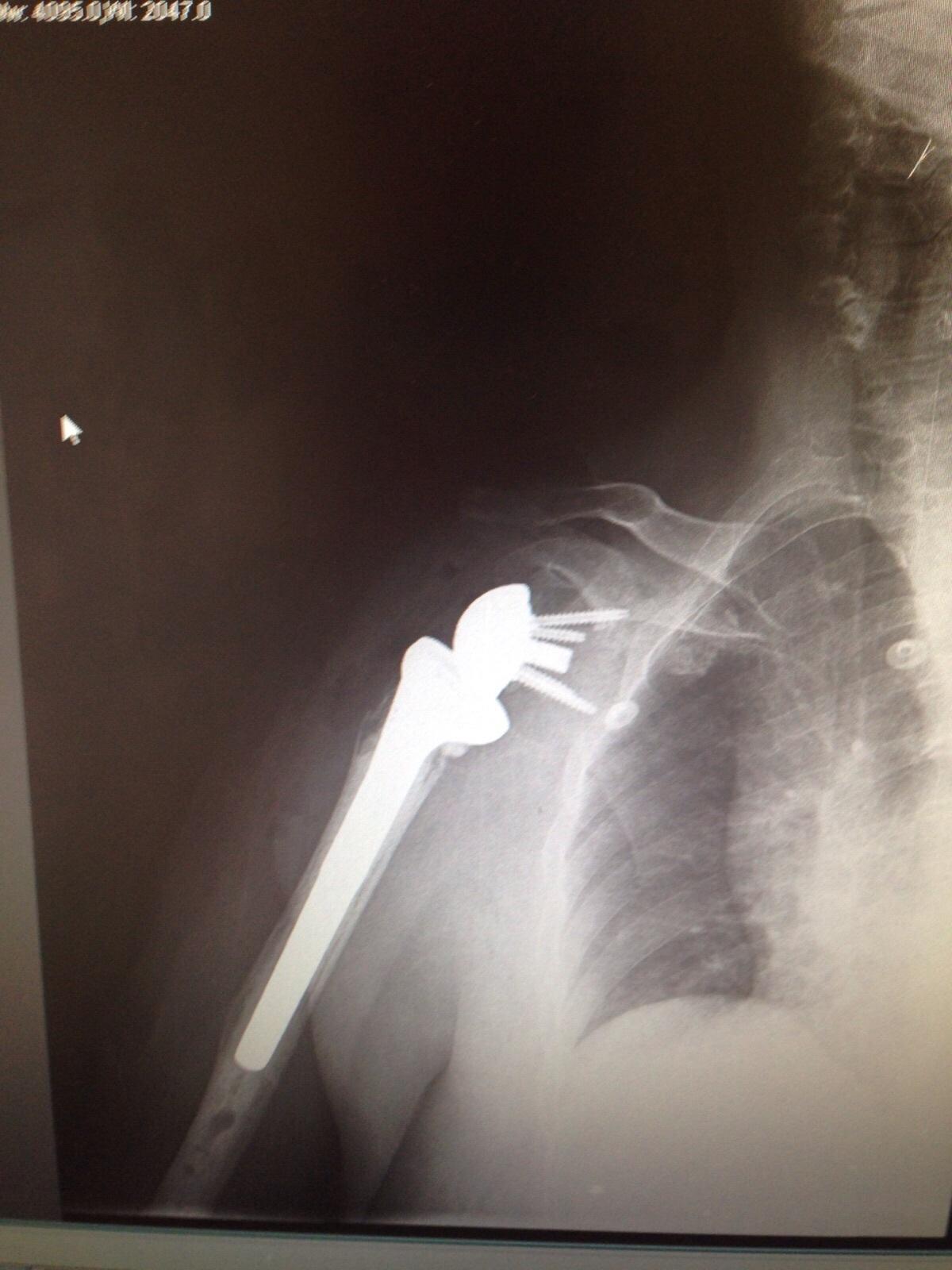
Accuracy of Patient-Specific Guided Implantation of the Glenoid Component in Reversed Shoulder Arthroplasty.
Fuente
Este artículo es publicado originalmente en:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29505820
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877056818300677
De:
Verborgt O1, Hachem AI2, Eid K3, Vuylsteke K4, Ferrand M5, Hardy P5.
Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2018 Mar 2. pii: S1877-0568(18)30067-7. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2018.01.010. [Epub ahead of print]
Todos los derechos reservados para:
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Masson SAS.
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
The aim of this study was to assess the accuracy of patientspecific guided glenoid component implantation in reverse shoulder arthroplasty MATERIALS AND METHODS: 32 reverse shoulder arthroplasties were done using pre-operative 3D planning and 4 patient-specific guides to prepare the glenoid and position the glenoid component. Baseplate version, inclination and entry point as well as angulation of the screws were compared to the pre-operative plan measured on CT by independent observers.
CONCLUSIONS:
Patient-specific instrumentation (PSI) for the glenoid component in reverse shoulder arthroplasty allows the shoulder surgeon to accurately execute the pre-operative 3D plan.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Masson SAS.
KEYWORDS:
Arthroplasty; Glenoid; Patient-Specific Targeting Guides; Reverse; Shoulder
Resumen
ANTECEDENTES:
El objetivo de este estudio fue evaluar la precisión de la implantación del componente glenoideo guiado del paciente en artroplastia de hombro invertida
MATERIALES Y MÉTODOS:
32 artroplastias inversas del hombro se realizaron con planificación 3D preoperatoria y 4 guías específicas del paciente para preparar la glenoides y posicionar la glenoides componente. La versión de la placa base, la inclinación y el punto de entrada, así como la angulación de los tornillos, se compararon con el plan preoperatorio medido en CT por observadores independientes.
CONCLUSIONES:
La instrumentación específica del paciente (PSI) para el componente glenoideo en la artroplastia de hombro invertida permite al cirujano de hombro ejecutar con precisión el plan 3D preoperatorio.
Copyright © 2018. Publicado por Elsevier Masson SAS.
PALABRAS CLAVE:
Artroplastia; Glenoideo; Guías de orientación específicas del paciente; reversa, hombro
- PMID: 29505820 DOI: 10.1016/j.otsr.2018.01.010